A LEYBOLD GmbH foi fundado em 1850 pelo alemão Ernst Leybold na cidade de Colônia – Alemanha. A princípio a produção era voltada exclusivamente para ensino de Física, porém a partir de 1906 houve uma expansão para linha de Tecnologia do Vácuo. Em 1988 foi fundado o grupo LD-Didactic, a qual engloba apenas a área didática, separando-se assim das soluções em vácuo. Atualmente o grupo LD-Didactic é líder mundial no ramo de Ensino em Ciências Naturais, atuando em mais de 80 países.
No Brasil a DK8 Tecnologia Educacional, no mercado educacional há 16 anos, é revendedora exclusiva da Leybold Didactic, por meio de uma parceria entre duas empresas que valorizam a excelência no desenvolvimento de Soluções Educacionais inovadoras com padrões mundiais. Para conhecer todas as soluções desenvolvidas pela Leybold Didactic em Ciências, Química, Biologia, Tecnologia Automotiva, Elétrica e Energia renovável acesse: www.ld-didactic.de/en/products-solutions.html , e entre em contato conosco. https://dk8.com.brcontato/
Solução completa para Física Experimental à nível de graduação
Baseado na grade curricular da Universidade de São Paulo, a DK8 Tecnologia Educacional oferece a solução completa de Física Experimental para cursos de graduação em bacharelado ou licenciatura. Abordando desde os temas mais elementares da Física, que é essencial para o desenvolvimento do aluno ao longo de sua formação, até técnicas avançadas específicas para análise de materiais, como por exemplo Física de raios X e Fotônica. Os conjuntos são recomendados para grupo de até 3 alunos.
P1.1.1.1 – Measuring lenghts: caliper gauge and micrometer
P1.2.4.1 – Fixed pulley, loose pulley and block and tackle as simple machines
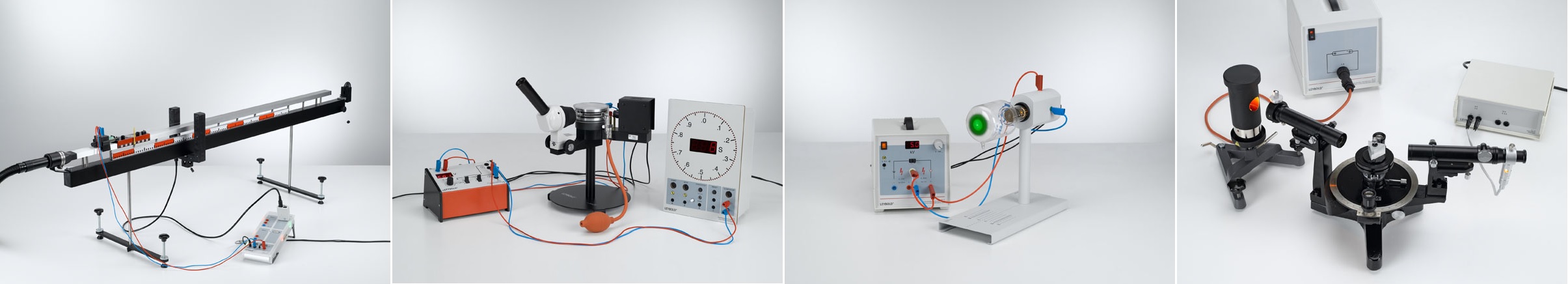
P1.3.5.4 – Free fall: Recording and evaluating with VideoCom
P1.4.5.2 – Moment of inertia and body shape
P1.7.6.1 – Investigating the Doppler effect with ultrasonic waves
P2.1.1.2 – Thermal expansion of solids – Measuring using the expansion apparatus
P2.3.2.1_c – Determining the specific heat of solids
P3.1.2.1 – Confirming Coulomb’s law – Measuring with the torsion balance, Schürholz design
P3.1.3.3_c – Measuring the potential inside a plate capacitor
P3.3.4.1_b – Measuring the magnetic field for a straight conductor and on circular conductor loops
P5.6.3.2 – Determining the velocity of light in various materials
P3.7.4.1 – Directional characteristic and polarization of microwaves in front of a horn antenna
P3.2.3.1 – Ohm’s and Kirchhoff’s Laws
P3.6.1.1_a – RC and RLC Circuits
P3.8.5.1 – Investigating the deflection of electrons in electrical and magnetic fields
P5.3.1.7 – Diffraction at a double slit and multiple slits – Recording and evaluating with VideoCom
P6.1.3.1 – Determining the specific charge of the electron
P6.1.5.1 – Diffraction of electrons at a polycrystalline lattice (Debye-Scherrer diffraction)
P5.7.2.1 – Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a grating spectrometer
P6.2.4.2 – Franck-Hertz experiment with mercury – Recording and evaluation with CASSY
P6.5.3.1_b – Nuclear magnetic resonance in polystyrene, glycerin and Teflon
P7.2.1.1_a – Investigating the Hall effect in silver
Relação de experimentos sugeridos em acordo com a grade curricular dos cursos de bacharelado ou licenciatura em Física. A solução possui diferentes configurações, com as opções de aquisição de dados manual ou assisitdo por computador (interface CASSY).